Delving into the realm of network security unveils a crucial aspect of our digital world. From safeguarding sensitive information to thwarting potential threats, the landscape of network security is both complex and vital for businesses and individuals alike. This guide on best practices for network security aims to shed light on the fundamental principles and strategies essential for fortifying networks in today's interconnected environment.
Importance of Network Security
In today's digital landscape, network security plays a crucial role in safeguarding sensitive information and ensuring the smooth operation of businesses and individuals. Without proper security measures in place, networks are vulnerable to a myriad of risks and threats that can have severe consequences.
Potential Risks and Threats
- Malware: Malicious software designed to infiltrate networks, steal data, and disrupt operations.
- Phishing Attacks: Deceptive emails or messages that trick users into revealing confidential information.
- Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks: Overwhelming a network with traffic to disrupt services and cause downtime.
- Data Breaches: Unauthorized access to sensitive data leading to theft or exposure of confidential information.
Impact of Network Security Breach
- Financial Loss: Businesses can suffer significant financial losses due to downtime, legal fees, and damage to reputation.
- Reputation Damage: A security breach can tarnish the reputation of a business or individual, leading to loss of trust from customers and partners.
- Data Loss: The loss of important data can have long-term consequences, affecting operations and decision-making.
- Legal Consequences: Non-compliance with data protection regulations can result in legal penalties and fines.
Fundamentals of Network Security
Network security is essential to protect sensitive information and prevent unauthorized access to networks. It involves implementing measures to secure the network infrastructure and data from cyber threats. Let's delve into the basic principles of network security, common security protocols, and encryption methods used to safeguard data in transit.
Basic Principles of Network Security
- Access Control: Limiting access to authorized users and devices to prevent unauthorized entry.
- Firewalls: Acts as a barrier between internal and external networks to filter incoming and outgoing traffic.
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): Monitors network traffic for suspicious activities or security threats.
- Virtual Private Network (VPN): Establishes a secure connection over the internet to protect data during transmission.
Common Security Protocols
- Secure Socket Layer (SSL): Provides secure communication over the internet by encrypting data transmitted between servers and clients.
- Transport Layer Security (TLS): An updated version of SSL that ensures secure communication between devices over a network.
- Internet Protocol Security (IPsec): Secures internet communication by authenticating and encrypting each IP packet.
Encryption Methods for Data in Transit
- Symmetric Encryption: Uses a single key to encrypt and decrypt data, suitable for fast and secure communication.
- Asymmetric Encryption: Involves a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption, ensuring secure data transmission.
- Hashing: Converts data into a fixed-length string of characters, used to verify the integrity of transmitted data.
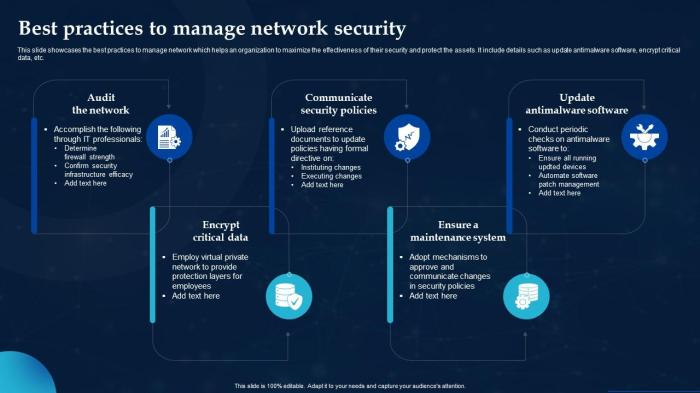
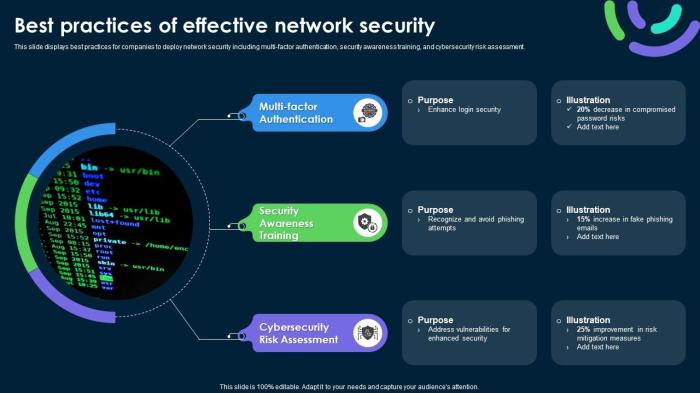
Best Practices for Network Security
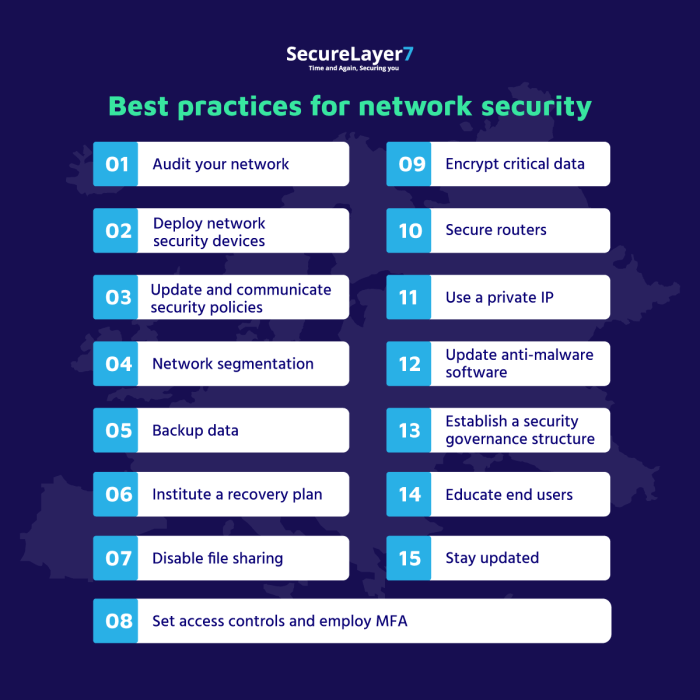
When it comes to securing network infrastructure, there are several best practices that organizations can implement to protect their data and systems from cyber threats. These practices include strong password policies, multi-factor authentication, firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and antivirus software.
Strong Password Policies and Multi-factor Authentication
Implementing strong password policies is essential for protecting network security. Organizations should require employees to use complex passwords that are regularly updated. Additionally, multi-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide two or more forms of verification before accessing sensitive information.
Firewalls
Firewalls act as a barrier between a trusted internal network and untrusted external networks, monitoring and controlling incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules. They help prevent unauthorized access to the network and block malicious traffic.
Intrusion Detection Systems
Intrusion detection systems (IDS) monitor network traffic for suspicious activity or security policy violations. They can detect and respond to potential threats in real-time, alerting administrators to take action to prevent security breaches.
Antivirus Software
Antivirus software is designed to detect, prevent, and remove malware from computers and networks. Regularly updating antivirus programs and running scans can help identify and eliminate viruses, worms, and other malicious software that could compromise network security.
Network Security Tools and Technologies

In today's digital landscape, where cyber threats are constantly evolving, it is crucial for organizations to leverage the latest tools and technologies to enhance their network security and protect their valuable data.
Network Monitoring Tools for Detecting Suspicious Activities
Network monitoring tools play a vital role in detecting and preventing suspicious activities that could potentially compromise network security. These tools continuously monitor network traffic, identify anomalies, and alert administrators of potential threats. Some popular network monitoring tools include:
- Wireshark: A widely-used packet analyzer that captures and analyzes network traffic in real-time.
- Nagios: An open-source network monitoring tool that provides comprehensive monitoring and alerting services.
- Splunk: A powerful platform for collecting, searching, and analyzing machine-generated data to detect security incidents.
Comparison of Cybersecurity Solutions for Network Protection
When it comes to network protection, there are various cybersecurity solutions available in the market. It is essential for organizations to choose the right solution based on their specific needs and requirements. Some common types of cybersecurity solutions for network protection include:
- Firewalls: Act as a barrier between internal network resources and external threats, filtering incoming and outgoing traffic based on predefined security rules.
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) and Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS): Monitor network traffic for suspicious activities and take action to prevent potential security breaches.
- Virtual Private Networks (VPNs): Securely connect remote users or branch offices to the main network through encrypted tunnels, ensuring data confidentiality and integrity.
Concluding Remarks
As we wrap up our exploration of best practices for network security, it becomes evident that a proactive approach to securing networks is paramount in safeguarding valuable data and maintaining operational integrity. By implementing robust security measures, adhering to stringent protocols, and staying abreast of evolving threats, individuals and organizations can navigate the digital landscape with confidence and resilience.
Popular Questions
What are the key components of network security?
Network security encompasses various elements such as firewalls, encryption, intrusion detection systems, and antivirus software to protect against unauthorized access and cyber threats.
Why is multi-factor authentication important for network security?
Multi-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of verification, reducing the risk of unauthorized access even if passwords are compromised.
How often should network security protocols be updated?
It is recommended to regularly update network security protocols to address new vulnerabilities and stay ahead of emerging threats. Quarterly or bi-annual updates are common practices.