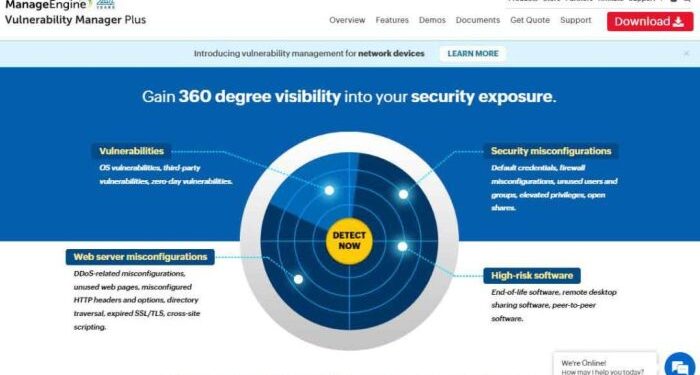
Exploring the world of managing security vulnerabilities in software, this guide delves into the importance of identifying, prioritizing, and resolving these vulnerabilities. From common types to best practices, this topic covers it all.
Understanding Security Vulnerabilities in Software
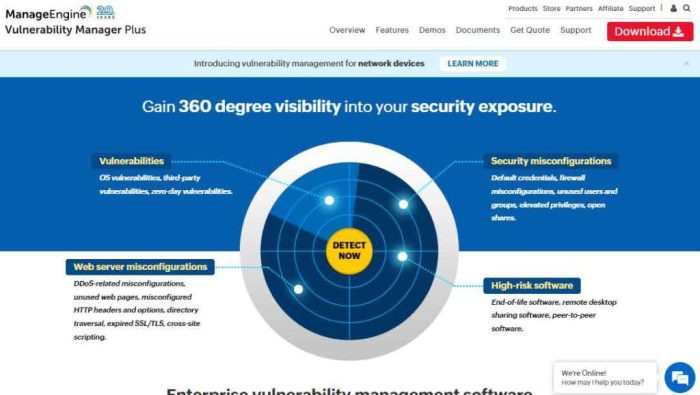
Security vulnerabilities in software refer to weaknesses or flaws in the design, implementation, or configuration of a software system that could be exploited by attackers to compromise the security of the system.
It is crucial to identify and address security vulnerabilities in software development to prevent potential security breaches, data leaks, unauthorized access, and other cyber threats that could result in financial losses, damage to reputation, and legal implications for organizations.
Common Types of Security Vulnerabilities
- Buffer Overflow: This occurs when a program tries to write more data to a buffer than it can hold, leading to potential code execution or system crashes.
- SQL Injection: Attackers can manipulate SQL queries to gain access to sensitive data or execute unauthorized actions on a database.
- Cross-Site Scripting (XSS): Allows attackers to inject malicious scripts into web pages viewed by other users, potentially stealing sensitive information or hijacking user sessions.
- Remote Code Execution: Attackers exploit vulnerabilities to execute arbitrary code on a targeted system, gaining control over the system and potentially causing damage.
Techniques for Identifying Security Vulnerabilities
When it comes to identifying security vulnerabilities in software, there are several key techniques that can be utilized to ensure the safety and integrity of the system.
Code Review
Code review involves manual inspection of the source code to identify potential security issues. This method allows developers to spot vulnerabilities early in the development process and address them before they become significant threats.
Penetration Testing
Penetration testing, also known as ethical hacking, involves simulating real-world attacks on a system to identify vulnerabilities. This proactive approach helps to uncover weaknesses that malicious actors could exploit, allowing for preemptive measures to be taken.
Static Analysis
Static analysis tools analyze the source code without executing it, looking for patterns and potential vulnerabilities. These tools can quickly scan the codebase for common security issues, such as SQL injection or cross-site scripting, helping developers identify and fix problems efficiently.
Importance of Automated Tools
Automated tools play a crucial role in identifying security vulnerabilities efficiently by automating the process of scanning and analyzing code. These tools can quickly detect common vulnerabilities, reduce human error, and provide developers with actionable insights to improve the overall security posture of the software.
Best Practices for Continuous Monitoring
- Implementing automated security testing as part of the continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipeline.
- Regularly updating dependencies and libraries to patch known vulnerabilities.
- Utilizing intrusion detection systems to monitor network traffic and detect suspicious activities.
- Engaging in threat intelligence sharing to stay informed about emerging security threats.
Managing and Prioritizing Security Vulnerabilities
When it comes to managing and prioritizing security vulnerabilities in software, the process typically involves assessing the vulnerabilities based on their severity and impact on the system. This allows organizations to prioritize which vulnerabilities need to be addressed first to minimize the risk of potential security breaches.
Assessing and Prioritizing Vulnerabilities
One common approach to prioritizing security vulnerabilities is to use the Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS), which assigns a score to each vulnerability based on factors such as exploitability, impact, and affected users. Vulnerabilities with higher CVSS scores are usually addressed first due to their potential to cause significant harm.
Organizations may also consider the likelihood of a vulnerability being exploited in the wild, the potential impact on sensitive data or systems, and regulatory compliance requirements when prioritizing vulnerabilities for remediation.
Creating a Vulnerability Management Plan
Creating a vulnerability management plan involves defining processes and procedures for identifying, assessing, and remediating security vulnerabilities in software. This plan should Artikel the roles and responsibilities of team members, the tools and technologies used for vulnerability management, and the timeline for addressing identified vulnerabilities.
Regular vulnerability scans, penetration testing, and code reviews are often part of the vulnerability management plan to ensure that new vulnerabilities are promptly identified and mitigated
Tools and Software for Managing Vulnerabilities
There are various tools and software available to help organizations manage and track security vulnerabilities effectively. Some popular examples include:
- Qualys: A cloud-based vulnerability management platform that offers continuous monitoring and assessment of vulnerabilities across the network.
- Nessus: A widely-used vulnerability scanner that helps identify security issues in the network, web applications, and databases.
- OpenVAS: An open-source vulnerability scanner that provides comprehensive vulnerability assessment and management capabilities.
Mitigating and Resolving Security Vulnerabilities
Once security vulnerabilities are identified in software, it is crucial to take immediate action to mitigate and resolve them to prevent potential exploitation by malicious actors.
Steps Involved in Mitigating Security Vulnerabilities
When a security vulnerability is discovered, the following steps are typically involved in mitigating the issue:
- Conduct a thorough analysis of the vulnerability to understand its scope and potential impact.
- Develop a patch or fix to address the vulnerability in the software code.
- Test the patch to ensure that it effectively resolves the vulnerability without causing any unintended consequences.
- Deploy the patch to all affected systems to eliminate the security risk.
- Monitor the software for any signs of exploitation or recurrence of the vulnerability.
Role of Developers, Security Teams, and Stakeholders
Resolving security vulnerabilities in software is a collaborative effort involving developers, security teams, and stakeholders:
- Developers:Developers play a crucial role in quickly developing and implementing patches to fix security vulnerabilities in the software.
- Security Teams:Security teams are responsible for identifying vulnerabilities, coordinating the response, and ensuring that the necessary security measures are in place.
- Stakeholders:Stakeholders, including management and users, need to be informed about the security vulnerabilities and the actions being taken to resolve them.
Successful Strategies for Resolving Security Vulnerabilities
Effective strategies for resolving security vulnerabilities in software include:
- Implementing a proactive security testing process to identify vulnerabilities before they can be exploited.
- Establishing a response plan with clear roles and responsibilities for addressing security vulnerabilities in a timely manner.
- Regularly updating software to patch known vulnerabilities and improve overall security posture.
- Engaging with the security community to stay informed about emerging threats and best practices for vulnerability management.
Last Recap
In conclusion, managing security vulnerabilities in software is a critical aspect of software development. By understanding, identifying, and mitigating these vulnerabilities effectively, organizations can enhance their overall security posture and protect their systems from potential threats.
Top FAQs
What are the common types of security vulnerabilities in software?
Common types include SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and insecure direct object references.
Why is it crucial to continuously monitor and detect security vulnerabilities in software?
Continuous monitoring helps in identifying new vulnerabilities that may arise due to changes in the software or external factors.
How can organizations prioritize security vulnerabilities based on severity?
Organizations can prioritize vulnerabilities by assessing the potential impact on data and systems, classifying them as high, medium, or low severity.